Contents
- Sign up on Google Cloud Platform Free Tier
- Create virtual machine instance
- SSH in browser and terminal
- Install NVIDIA GPU driver and toolkit
- Docker and Nvidia-docker
- Install Docker and Nvidia-docker
- Install Anaconda
- Install additional packages
1. Sign up on Google Cloud Platform Free Tier
Click here to sign up for 12 months and $300 free credit to get you started. Always
Free products to keep you going.
2. Create ports in firewall
There two options to configure firewall for Jupyter notebook and Tensorboard.
- Option 1: VPC Network → Firewall rules

- Option 2: Create ports using command-line
# jupyter
gcloud compute firewall-rules create jupyter --allow tcp:8888-8889 --source-ranges 0.0.0.0/0
# tensorboard
gcloud compute firewall-rules create tensorboard --allow tcp:6006 --source-ranges 0.0.0.0/0
3. Create virtual machine instance.
Follow
@howkhang's instruction or @Allen Day's instruction to upgrade to paid account and create virtual machine instance. List the specification here.
- Request for increase in quota for GPU
- IAM & Admin → Quotas:
- Region: choose a zone with NVIDIA K80 GPU and Intel Broadwell CPU.
- Select NVIDIA K80 GPUs (without “preemptible”) → Edit Quotas → Change to “1” → Submit Request.
- Receive email approval of quota increase
- Create your virtual machine instance
- Compute Engine → VM instances → Create
- Cores: 4 vCPU
- Memory: 26 GB
- CPU platform: Intel Broadwell or later
- GPUs: 1 with NVIDIA Tesla K80
- Boot disk: Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, 250 GB (SSD charges extra money), I used 250 GB
- Firewall: Check 'Allow HTTP/HTTPS traffic'
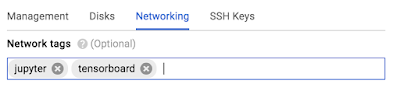
- Networking → Network tags: jupyter, tensorboard
- (Optional) Convert the IP address to static
- VPC network → External IP addresses: Convert IP address to “Static” and give it a name. (Static IP charges US$0.01/hour at time of writing).
 |
Estimated cost
|
3. SSH in browser and terminal
There are a few of methods to connect to your instance. See
Google official document here.
- Option 1: Connect in browser window
- Option 2: Connect in terminal
- Download and install Google Cloud SDK.
- Run “gcloud init“ to initialize and link to you account.
- Run “gcloud compute ssh <your instance name>”. <your instance name> is as same as the image shown in Option 1.
- (Option) to switch user, run command “gcloud compute ssh <your user name>@<your instance name>”
- SSH shall be connected successfully:
4. Install NVIDIA GPU driver and toolkit
I have written another tutorial to install NVIDIA driver, CUDA tookit and cuDNN library. Click and read this
Follow the steps to install NVIDIA driver, CUDA toolkit and cuDNN library.
If CUDA install is successful, running this command will display a table describing an available Tesla K80 GPU.
$ nvidia-smi
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 390.30 Driver Version: 390.30 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 Tesla K80 Off | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 33C P0 75W / 149W | 0MiB / 11441MiB | 89% Default |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: GPU Memory |
| GPU PID Type Process name Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
◎Set environment variables
Add the environment to
.bashrc under home directory.
export PATH=/usr/local/cuda/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
5. Install Docker and NVIDIA-docker with TensorFlow container
◎Install Docker and NVIDIA-docker
sudo apt-get -y install \
apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
#### Install Docker
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce
#### Install Nvidia Docker
curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/gpgkey | sudo apt-key add -
curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/ubuntu16.04/amd64/nvidia-docker.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-docker.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-docker2
sudo pkill -SIGHUP dockerd
◎Make sure docker container can see the GPU
sudo nvidia-docker run --rm nvidia/cuda nvidia-smi
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 390.30 Driver Version: 390.30 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 Tesla K80 Off | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 34C P0 71W / 149W | 0MiB / 11441MiB | 99% Default |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: GPU Memory |
| GPU PID Type Process name Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
◎Launch TensorFlow environment with Jupyter and Tensorboard
You can replace
tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-gpu with a specific built container.
#### [1] This will start container automatically
nvidia-docker run -dit --restart unless-stopped -p 8888:8888 -p 6006:6006 --name tensorflow tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-gpu jupyter notebook --allow-root
#### [2] This will start container manually
nvidia-docker run -it -p 8888:8888 -p 6006:6006 --name tensorflow tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-gpu jupyter notebook --allow-root
◎More containers
See all available tags for additional containers, such as release candidates or nightly builds.
◎List containers
$ nvidia-docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
cea9902468a5 tensorflow_gpu_jupyter "/run_jupyter.sh --a…" 8 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 0.0.0.0:6006->6006/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8888->8888/tcp tensorflow-py3
◎Launch a container
$ nvidia-docker start -ai <CONTAINER ID|NAME>
◎Stop a container
$ nvidia-docker stop <CONTAINER ID|NAME>
◎Delete a container
$ nvidia-docker rm <CONTAINER ID|NAME>
or
$ nvidia-docker rmi <IMAGE NAME>
◎More Docker commands
See all base commands for Docker
6. Install Anaconda
See official guide to install TensorFlow using Anaconda.
CONDA_INSTALL="Anaconda3-5.1.0-Linux-x86_64.sh"
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/${CONDA_INSTALL}
chmod +x ${CONDA_INSTALL}
./${CONDA_INSTALL}
Note that we say
yes here to add install location to
.bashrc
Do you wish the installer to prepend the Anaconda3 install location
to PATH in your /home/chunming/.bashrc ? [yes|no]
[no] >>> yes
...
### Remember to run this.
$ source ~/.bashrc
◎Create an environment
conda create -n tensorflow-py3 pip python=3.6
source activate tensorflow-py3
◎Install TensorFlow
Option 1: Recommended
Choose a TensorFlow python package at here. Replace the TF_URL with the URL you picked.
TF_URL=https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/linux/gpu/tensorflow_gpu-1.9.0-cp36-cp36m-linux_x86_64.whl
pip install --ignore-installed --upgrade $TF_URL
Option 2: Use Conda
conda install -c conda-forge tensorflow-gpu
Option 3: Use pip
pip install tensorflow-gpu
7. Install additional packages
To install packages, you can run
pip install since you've activated the environment.
pip install matplotlib opencv-python scikit-image PILLOW sklearn keras
8. Error Message
You may encounter an error like Importerror libcublas.so.9.0 cannot open shared object file no such file or directory or ImportError: libcudnn.so.7: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory during the installation.
◎Uninstall old version of CUDA Toolkit
Assume that we have older version of CUDA and cuDNN 6.
sudo apt-get purge cuda
sudo apt-get purge libcudnn6
sudo apt-get purge libcudnn6-dev
After uninstallation, repeat the steps of CUDA and cuDNN installation.
◎Add environment variables
Set up the development environment by modifying the PATH and LD_LIBRARY_PATH variables, also add them to the end of .bashrc file
export PATH=/usr/local/cuda-9.0/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda-9.0/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
◎Reboot the system to load the NVIDIA drivers.
I encountered an error
ImportError: libcublas.so.10.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory since upgraded to cuda 10 and cudnn 7.5. Follow
fabricatedmath's instruction to fix the problem
conda install cudatoolkit
conda install cudnn
9. Test
See
how to use GPU in TensorFlow official guide
import tensorflow as tf
# Creates a graph.
a = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0], shape=[2, 3], name='a')
b = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0], shape=[3, 2], name='b')
c = tf.matmul(a, b)
# Creates a session with log_device_placement set to True.
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True))
# Runs the op.
print(sess.run(c))
**IMPORTANT: Remember to shutdown your VM instance when you're done or you will incur charges.**
References






























